Electronics Manufacturing Services are the backbone of manufacturing for companies to produce devices that are launched into the market. They take care of the backend operations from the very beginning of design to delivery and they are crucial at several stages of production. Read more to find out about the challenges that may occur during the manufacturing process.
Electronics have been bulldozing their way into every field replacing several manual systems that require manpower. A well-established fact that machines are more reliable, accurate and fast and therefore mitigate errors has bolstered the popularity of electronics. From the manufacturing sector to everyday living, its applications are extensive.
The process of Electronics Manufacturing
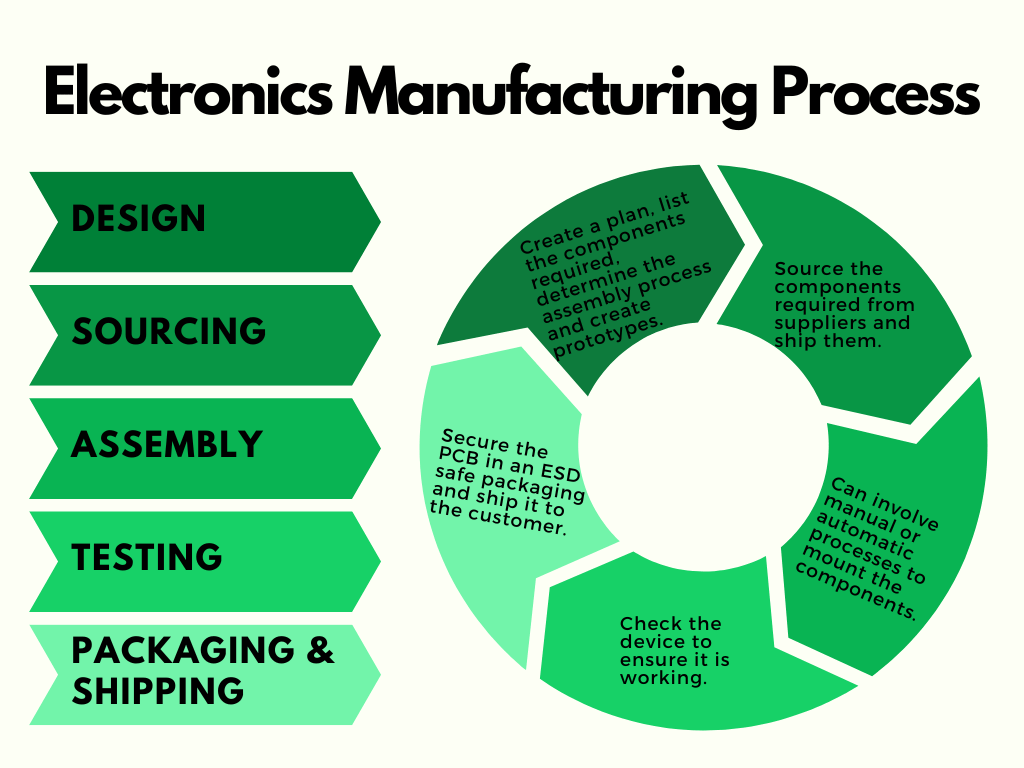
The key elements in an electronics manufacturing process begin from designing the devices to testing and shipping them to customers. Various factors are to be taken into consideration when manufacturing products for OEMs and enterprises. A good design, reducing PCBA re-operations & iterations, and finally controlling material and labour costs contribute to the cost-effectiveness of the product.
The article on Small-run SMT production or Building prototypes using manual soldering gives you a detailed step-by-step understanding of the semi-automatic and manual assembly of PCBs.
Let’s explore the challenges that an EMS provider might face during the stages spanning from product design, development, and production to launching it in the market.
-
The constant and rapid advancements in technology:
The advancement in technology has become a challenge to most manufacturing companies. Companies have been investing heavily in research to update their existing product or launch new ones to stay ahead of competitors
-
Adopting design principles:
Design principles when adopted during the early stages of planning would be efficient and cut costs and increase lead times. A good design is essential to the functionality, reliability and durability of a device.
-
Product shelf life:
With the advancements in technology, companies face the irony of a time-bound product life cycle for non-perishable goods. There are more and more innovative products that are launched every so often that encourage a switch to replace existing products. For example in PCB manufacturing, SMT has been evolving rapidly and so are the machines. Pick and place machines are becoming faster, more flexible to incorporate changes, and more precise and reliable.
-
Reliability of the device:
The reputation of both the manufacturer and EMS provider relies on the reliability and functionality of an electronic device. The durability and reliability of electronic devices rely on several factors. Although the poor design, quality and manufacturing defects are major factors, environmental conditions, overstress and wear and tear also may contribute to the device’s reliability.
-
Access to suppliers:
Building a strong network to source components and having consistent supply are crucial to the manufacturing and delivery of a product. Even when EMS providers have access and a network of efficient suppliers sometimes there are unavoidable crises that affect the supply. E.g. the recent chip shortage that shook the automotive industry. The unfortunate turn of events during COVID-19 disrupted both the production and shipping of automobile chips. This delayed the launch of several new and old model vehicles.
-
Supply chain disruptions:
Although production is crucial to launch products, supply chain management is important too. Quoting the example from the above point, the production of the chips that relied on components sourced from suppliers was delayed due to the disruptions in the supply chain. This in turn delayed the production of the chips and their delivery to the automobile manufacturers. The global shipping delays resulted in production and launch setbacks of vehicles.
-
Economic volatility:
The manufacturing process is susceptible to the global economic fluctuations that occur. This results in price variations and sometimes leads to orders being cancelled or withheld. When raw material is required certain rare or high-in-demand materials to build a device which might be difficult to obtain. This might lead to a shortage and retailers may bump up the prices.
-
Competition:
This is an unavoidable yet difficult challenge to tackle. With the rise in the number of competitors, EMS providers have to battle with quotes which may sometimes not be very profitable. But this can lead to continuous orders which in the long run would be profitable.
-
Labour issues:
Although the manufacturing industry has become technologically advanced, it still requires a huge amount of manpower in several or a few stages of the manufacturing process. There could be manpower shortages, labour strikes due to economic fluctuations, working overtime to meet an increase in demand, etc. Since we still highly rely on labour-centric production processes, they are key to smooth production and supply processes.
-
Sustainability:
The world is moving towards including “sustainability” in all spheres of life. E.g. There are several communities that produce living necessities and live isolated from the rest of the world. There have been several protests and movements against several industries to become more sustainable. Several factories have been trying to become fully solar-powered, have greener manufacturing processes, improve inventory management and cut wastage, use recycled material, etc.
-
Emerging markets:
Several developing nations have been striving to become more advanced by increasing their standardisation and production. They are rapidly increasing their per capita income due to high production levels and significant industrialisation.
-
Project recall:
After launching a product, sometimes manufacturers detect defect(s) and would publicly make an announcement to all their customers to return the product. This does affect the reputation of the brand and they pay a price with a drop in overall sales at least temporarily until damage control is executed.
-
Social media pressure:
Today, most customers raise complaints on social media platforms when companies don’t respond effectively. On the same hand, some customers give positive feedback and voluntarily promote a certain product. Social media can work both ways; for or against the reputation of a product. Moreover, social media has become a primary source of advertisement today. Many brands have been creating interactive content making ads more engaging and interesting, this puts pressure on competitive brands to follow the trend.
-
Competitive prices:
Irrespective of overall costs incurred for a product from design to delivery, electronics manufacturers have to quote prices that are attractive to product manufacturers. This spirals down to cutting costs in several other stages of manufacturing and sometimes causes disruptions in the manufacturing process.
-
Warranty and extended support:
Consumers can choose from a number of brands that exist these days. Electronic devices come at competitive prices and value-added services have become one of the deciding factors. Warranty and customer support are important as customers weigh in the service and support response and time period. Each brand varies from one another and this has become critical to the sales of a product. However, this is an added cost to the manufacturer and hence the reliability of the product is crucial




